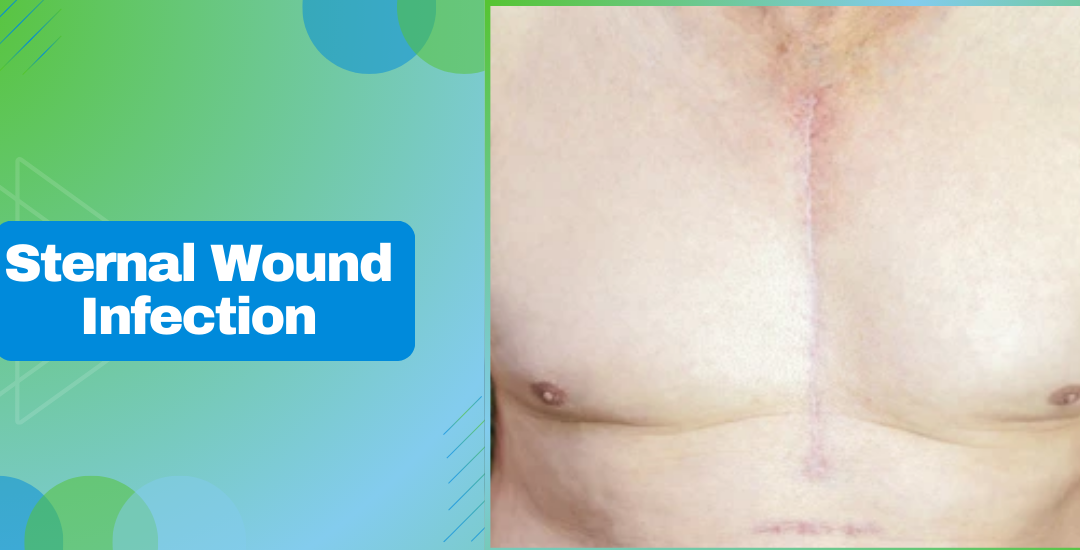
The sternal region, located at the center of the chest, plays a crucial role in chest stability and protection of vital organs such as the heart and lungs.
“The sternum or breastbone and its surrounding structures are critical for the structural integrity of the chest. It is an anchor point for several major muscles involved in breathing and upper body movement. Issues in the sternal region can significantly impact daily life, particularly when faced with complications like Sternal Wound Infection (SWI).” says Dr. Leena Jain, a renowned plastic surgeon in Mumbai.
Dr. Leena Jain offers advanced treatments for SWI, ensuring comprehensive care and optimal recovery. Her expertise in innovative surgical approaches helps patients regain function and reduce the risk of further complications.
Did You Know?
High Risk with Heart Surgery: Up to 5% of heart surgery patients may develop a sternal wound infection.
Are you concerned about a potential SWI or looking for preventive guidance? Reach out to your healthcare provider today to ensure your post-surgical recovery is on track.
Let’s dive into the details.
What is a sternal wound infection?
SWI is a severe complication that can occur along the sternum (breastbone) after chest surgeries, such as open-heart surgery. This infection can develop when bacteria invade the surgical site, leading to inflammation and potential complications.
Dr. Leena Jain, a proficient plastic surgeon in Borivali, adds:
“A sternal wound infection impacts the tissue around the sternum. It can vary in severity from superficial infections to deeper, more serious ones affecting the bone, known as osteomyelitis. Effective management is crucial to prevent progression, deeper tissue damage, and other systemic effects.”
How can you tell if it’s more severe than it seems? Let’s find out!
Symptoms of deep sternal wound infection
Here are the symptoms of deep SWI you should watch out for:
- Increased pain around the sternum that worsens over time and does not respond well to usual pain management
- Persistent fever along with chills is common, indicating that the body is fighting a severe infection
- Redness and swelling around the sternum indicate the infection progression
- Purulent discharge of pus or other fluids may begin to drain from the site of the surgery
- The sternum may feel unstable or move when touched or when you move or when you breathe, indicating that the infection has affected the bone
- A foul odor may emanate from the infection site, indicating a possible bacterial infection.

These symptoms require immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
Mumbai’s trusted Reconstructive Microsurgeon, Dr. Leena Jain, cautions:
“Deep sternal wound infection can lead to the breakdown of the surgical incision and the underlying bone. This breakdown weakens the structural integrity of the sternum, resulting in sternal wound dehiscence, which is the separation or instability of the breastbone.”
Let’s dig deeper into why these infections occur.
Causes of sternal wound infection
SWIs arise from several factors:
- Bacterial contamination which may occur during or after surgery
- Poor surgical techniques, such as inadequate sterilization or improper handling during the procedure
- A weakened immune system which makes patients more vulnerable to infections
- Underlying medical conditions like diabetesor obesity which impair wound healing due to poor circulation
- Use of medical devices like sternal wires or pacemakers that may harbor bacteria
- Insufficient postoperative care and monitoring after surgery which may hamper proper healing
These factors highlight the importance of stringent sterile techniques, careful monitoring, and appropriate patient care before and after surgery to minimize the risk of SWIs.
Are you more susceptible to these infections? Let’s consider the risk factors.
Risk factors of an infected sternum
Older patients often have a reduced immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections
Diabetes, as high blood sugar levels, can impair the body’s ability to heal
Excess body weight can strain the healing process, particularly in wound closure and immune function
Tobacco use impairs blood flow and wound healing
Prior chest surgeries can leave scar tissue, complicating healing and increasing infection chances
Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or the use of certain medications
Inadequate nutrition can weaken the body’s natural defense mechanisms against infection
Are you concerned about the risk of developing a sternal infection? Please visit a health professional for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.
Are you concerned about sternal wound infection after cardiac surgery? Please consult a skilled plastic surgeon for safe and reliable treatment options.
So, what can you do if you find yourself affected?
Treatment options
Effective management of SWI requires a multidisciplinary approach. It often involves cardiologists, infectious disease specialists, and surgeons to tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s needs. Treatment approaches include:
Surgical Debridement:
Surgical debridement involves removing infected and necrotic (dead) tissue from the wound. Reducing the load of infectious agents is crucial to promote healthier healing conditions. This procedure may need to be repeated to remove all infected material.
Vacuum-Assisted Closure (VAC) Therapy:
VAC is the application of a vacuum dressing to the wound, which uses negative pressure to enhance healing. This therapy helps reduce swelling, removes exudate and infectious materials, and promotes the formation of granulation tissue. This method is often used after debridement to aid in faster wound closure.
Muscle Flap Reconstruction:
Muscle flap reconstruction is the surgical reconstruction of the area using muscle flaps from the patient’s body. Surgeons employ this procedure to cover the defect when the infection has led to significant tissue loss. This not only improves the structural integrity of the chest wall but also enhances blood supply to the area, which is vital for healing.
Antibiotic Therapy:
The administration of antibiotics is the first line of treatment for controlling and eradicating the infection. They can be intravenous (through a vein) or oral, depending on the severity of the infection. The antibiotic type is typically determined by the bacteria identified in cultures taken from the wound.
Ongoing Wound Care:
Proper wound care, dressing change, and regular visits to a healthcare provider are essential to prevent re-infection and monitor the progress of wound healing.
As we wrap things up, here’s the key takeaway.
Conclusion
Sternal wound infections, while serious, are easily manageable thanks to advancements in medical technology and the dedication of healthcare professionals.
Dr. Leena Jain is deeply committed to improving patient outcomes with innovative treatments and refined surgical techniques. Focusing on personalized treatment plans ensures that patients receive comprehensive care, promoting healing and minimizing complications effectively.
FAQs
How do you treat an inflamed sternum?
Doctors typically prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain. Rest and avoiding strenuous activities are also crucial to prevent further irritation of the sternum area. In some cases, the doctor may recommend physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and gently support the healing process.
Why does my sternum hurt?
Sternum pain can be due to various factors, including:
- Physical trauma to the chest
- Inflammation of the costosternal joints (costochondritis)
- Conditions like SWI, especially following surgery
Activities that strain the chest muscles, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise, can also lead to discomfort in the sternum area.
What are the 4 signs and symptoms of a chest wound?
Signs and symptoms of a chest wound can include:
- Visible bleeding or discharge from the site
- Sharp or stabbing pain that may worsen with breathing or movement
- Swelling or bruising around the affected area
- In severe cases, difficulty breathing or a sucking sound from the wound when inhaling
Immediate medical attention is essential to manage these symptoms and prevent complications.